User Research
We aimed to incorporate a user-centered methodology throughout our research process. In the empathy stage, we conducted both secondary and primary research by engaging directly with street vendors. This process involved having in-depth conversations, which allowed us to gather valuable insights through fieldwork.

We met with the community and researched different sources, such as news articles and newspapers.
We discovered how they feel, what they think, do, and say regarding their work conditions.
We experienced their pains, needs, and each step they go through during the day.
We identified the insights, defined what we should solve, and outlined what we needed to build.

Empathy map
Customer journey map
It is an activity that requires constant movement.
They love their job.
80% of street vendors in La Plaza de Bolívar are elderly and primary household providers
It is an activity that requires constant movement.
The most effective way to secure a sale is by approaching people and engaging them in conversation about historical facts or local recommendations.
The biggest challenges that sellers experience during their shifts are repetitive movements and static physical positions, which cause tiredness, discomfort, and may possibly lead to health issues.
Monitoring their merchandise is the main reason why sellers get distracted during sales.
Design process
Focusing on constant engagement with the community, the design process was conducted and addressed with the help of the selected group.

Grip and posture analysis
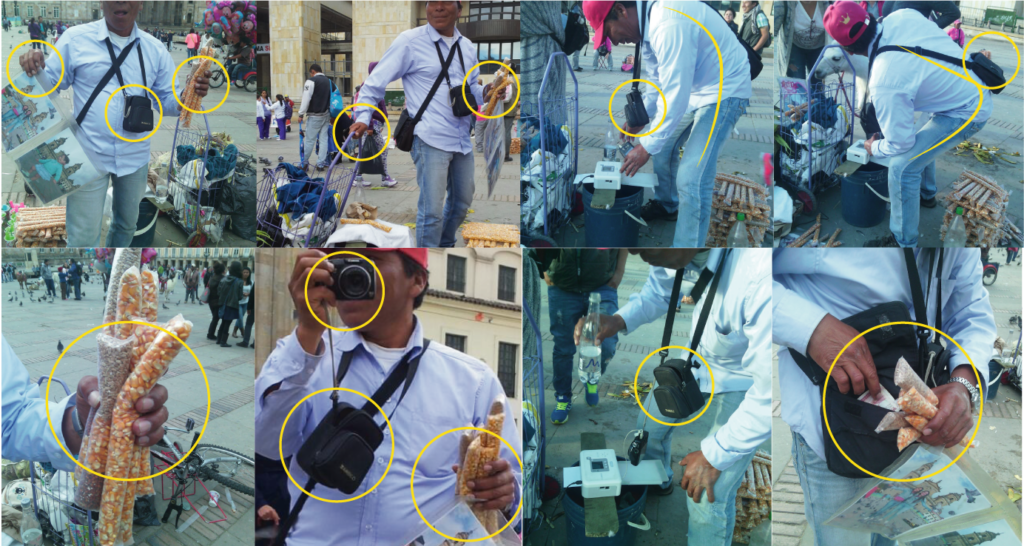

50% of the time, they remain in an upright posture.
90% of the time, they maintain a hand posture with a full-hand palmar grip and a three-finger pinch, both with excess weight.
100% of the time, they are carrying items on their body.
30% of the time, they remain in lumbar spine flexion, hip and knee flexion, a flexed posture, and a squatting posture.
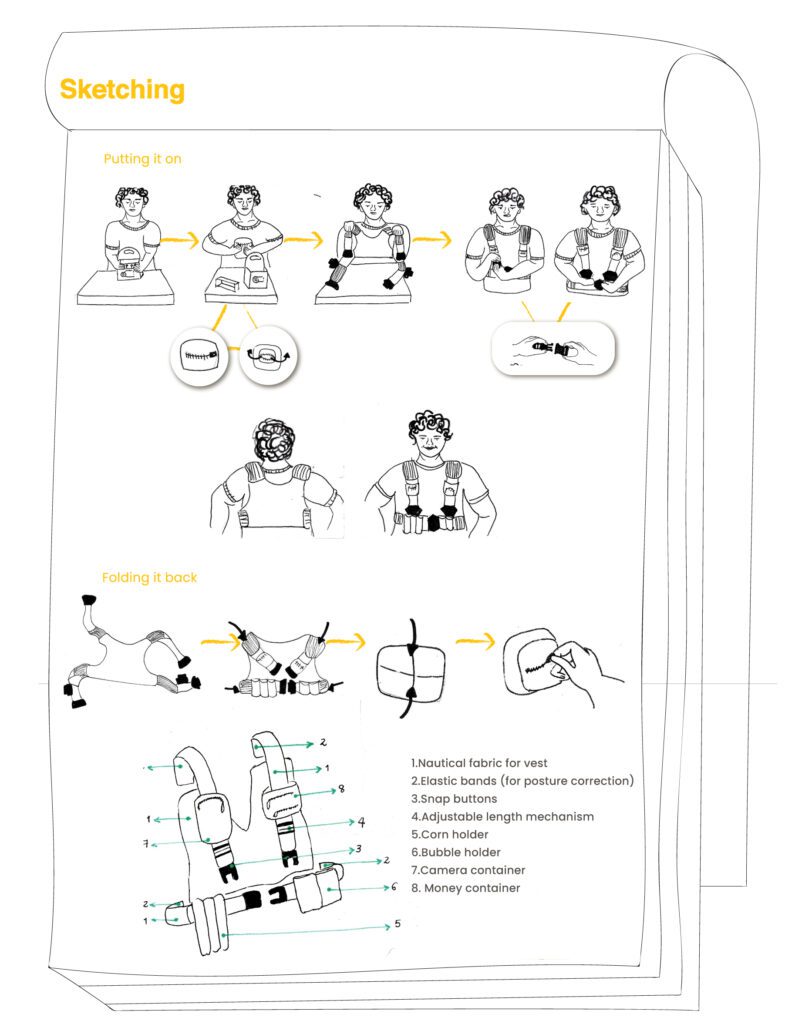
Takeaways:
Functional Design: Solving real problems such as posture and load significantly improves the users’ quality of life.
Social Impact: Design can highlight and address challenges rassociated with informal employment.
Applied Empathy: Understanding the user in their environment is key to creating effective solutions..
Lesson lernead:
Direct Observation: Interacting with real users generates unique insights.
Constant Iteration: Refining the design ensures it meets multiple needs.
Clear Purpose: Designing with social impact strengthens the project’s value.